Omron Power Supplies
Reliable Power Supplies with Predictive Maintenance and Data Management Capabilities.
Brochures
What factors should be considered when selecting Power Supplies?
Select Power Supplies based on the following factors.
1)What are Power Supplies’ input voltage specifications?
Example:
When the input voltage is 100 VAC, select a model with a 100 to 240 VAC range or automatic selection of 100 or 200 VAC.
2)What are the load’s DC voltage specifications?
Example:
Select a DC voltage such as 12 VDC or 24 VDC.
3)What is Power Supplies capacity requirement?
Example:
Select Power Supplies so that the maximum load capacity is less than the Power Supplies’ output capacity.
4)What is the mounting location and mounting method?
Example:
If it is important to save space in a control panel and Power Supplies will be mounted to a DIN Track, use Power Supplies such as the S8VS or S82K
5)Are advanced functions required?
You want to display the output current and monitor when Power Supplies are due for replacement.
→ S8VS Series
You want to use the remote sensing and remote control functions.
→ S82L, etc.
You want Power Supplies to support peak loads.
→ S82F-P Series
You want to use the overload protection function.
→ S82J (most models), S8TS, S8VS, S8PS, etc
You want to backup operation with batteries if the AC power input is interrupted.
→ S8TS Series or S8T-DCBU-01
What happens when the Power Supplies reach their life expectancy?
What is the best way to estimate the amount of heat produced by the Power Supply?
Equations:
Internal loss (W)
= Effective input power – Output power
= Output power/Efficiency – Output power
Note:Reducing the load rate is an effective way to reduce the amount of heat produced.
Example Calculating the Heat Produced by a 100-W S82K Switch Mode Power Supply
Power rate: 80%
Output power: 24 V × 4.2 A = 100.8 W
Effective input power: Output power/Efficiency = 100.8 W/80% = 126 W
Internal loss (heat produced): 126 W – 100.8 W = 25.2 W
To convert the internal loss to calories:
By Joule’s law, 1 W = 0.24 cal/s,
so 25.2 W = 25.2 × 0.24 cal/s = 6.05 cal/s
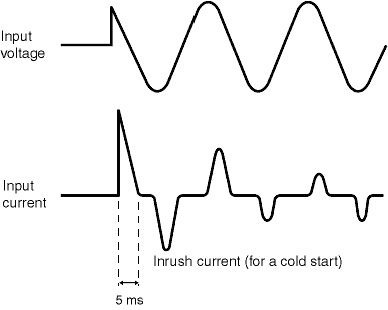
How long does the inrush current from the Power Supply continue to flow?
About 5 ms as a general rule. An inrush current will occur regardless of the load, even when there is no load.
Inrush Current
When the power is turned ON for a Switching Power Supply, a peak current flows to charge the input smoothing capacitor. This is called inrush current.
The inrush current value depends on the timing at which the power is turned ON, and on the inrush current prevention circuit, but it can be anywhere from several times to several tens of times higher than the input current during normal operation.
What is overload protection function?
This protection function prevents damage to the Power Supply itself due to overcurrent (including output short-circuits). The protection function is activated and the output current is limited when the load current is greater than the overcurrent detection value (this value depends on the model).
The output voltage will also drop according to the overload (load impedance).
The drop level depends on the overload conditions and load line impedance.
The following table shows the six types of output voltage drop characteristics for main models when the overcurrent protection function is operating.
These drop characteristics can be seen as indicating the limit on the output current that can be supplied to the load effectively in the process in which the output voltage starts when the AC input turns ON. When connecting a load (with built-in DC-DC converter) that starts operating from a low voltage or a capacitive load in which inrush current can flow easily, consider the trend in overcurrent protection drop characteristics and the startup characteristics on the load side when selecting the Power Supply.
Generally, an inverted L voltage drop is considered favorable at startup.
| Overcurrent drop characteristics |
Relationship between output voltage and output current |
Trend | Main models |
| Gradual current/ voltage drop |
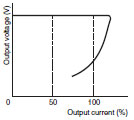 |
When a voltage drop occurs, the output current also gradually drops, and the output returns to the normal level automatically (automatic recovery) when the overcurrent status is cleared. |
S82K: 3 W, 7.5 W, 15 W S8VS: 15 W |
| Inverted L voltage drop |
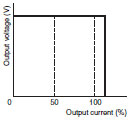 |
When a voltage drop occurs, the output current remains essentially constant. The output returns to the normal level automatically (automatic recovery) when the overcurrent status is cleared. |
S82J: 100 W (5 V, 12 V, 15 V), 150 W, 300 W S82K: 90 W, 100 W S8TS S8T-DCBU-02 S8VS: 240 W S8VM (12, 15, 24 V): 50 W, 100 W, 150 W, 300 W, 600 W, 1,500 W |
| Voltage/ current drop Intermittent operation |
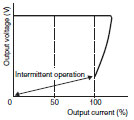 |
When a voltage drop occurs, the output current also gradually drops, and the load of the Power Supply itself is reduced (automatic recovery) using intermittent output when the voltage drops to a certain level or lower. |
S82J: 10 W, 25 W |
| Inverted L voltage drop Intermittent operation |
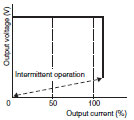 |
When a voltage drop occurs, the output current remains essentially constant. The load of the Power Supply itself is reduced (automatic recovery) using intermittent output when the voltage drops to a certain level or lower. |
S8VS: 30 W, 60 W, 90 W, 120 W, 180 W S8VM (5 V): 50 W, 100 W, 150 W, 300 W, 600 W |
| Gradual current increase/ voltage drop Intermittent operation |
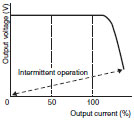 |
When a voltage drop occurs, the output current increases as the voltage drops, maintaining constant power, and the load of the Power Supply itself is reduced (automatic recovery) using intermittent output when the voltage drops to a certain level or lower. |
S82J: 50 W, 100 W (24 V) S82K: 30 W, 50 W S8VM: 15 W, 30 W |
| Inverted L voltage drop Shut off |
 |
When a voltage drop occurs, the output current remains essentially constant. If, however, the overcurrent status continues for longer than a fixed time, the output will be interrupted and the power will need to be turned ON again to recover. |
S82J: 600W |
Automotive Case Stufy
The customer replaced its power supply with the Omron S8VK-X, which provides 24/7 remote monitoring of power supply health via EtherNet/IP to help identify abnormal DC circuit issues.

Who is Mechatronic Solutions?
Mechatronic Solutions is a distributor of OMRON automation products and solutions for Minnesota, Wisconsin, North Dakota, and South Dakota. We have a team of technical experts on staff to help select the right automation products for your application. If you have any questions or would like to speak with a member of our team, contact us at (763) 447-3407 or fill in the Contact Form.
Why Omron Power Supplies?
OMRON provides many types of general-purpose Power Supplies, such as the type mounted to DIN rail or the type built into equipment. OMRON also provides the S8VS which provides notification of replacement timing, and the Buffer Block that handles momentary power interruptions, and other highly reliable Power Supplies.
In-House Assembly Services
Mechatronic Solutions specializes in providing contract manufacturing and assembly services including engineered subsystems for customers in a variety of industries. With design services to create subsystem solutions that fit seamlessly into existing processes and systems, Mechatronic Solutions can save you time, money and hassle in your manufacturing operations.
Some of Omron’s Power Supplies
- S8VK-WA/B
- S8VK-G
- S8VK-X
- S8VK-S
- S8FS-G
CONTACT MECHATRONIC SOLUTIONS TODAY
Need power supplies and panel work in Minnesota, Wisconsin, North Dakota, or South Dakota… Call Mechatronic Solutions at 763-447-3407 or fill in the Contact Us form today to work with our application engineers or schedule a demo.
